文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Promise是什么?
- 二、Promise核心逻辑实现
- 1.基本原理
- 2.新建类promise类,传入执行器executor
- 3.传入resolve和reject方法
- 4.then方法的简单实现
- 5.完整代码及验证
- 6.代码改进
- 三.链式调用
- 1.链式调用实现的基本思路
- 2.then方法返回promise对象
- 3.resolvePromise方法
- 四.总结
前言
ES6无异于是当前前端必备的一项技能,而Promise又是ES6里面的重中之重,Promise充斥在我们代码的每一个角落。
一、Promise是什么?
promise是一种异步编程解决方案,主要解决了:当有先后依赖的多个异步任务时,层层嵌套的回调写法不灵活、容易滋生bug、且难以维护的问题。
目前我们使用的 Promise 是基于 Promise A+ 规范实现的。所以我们接下来的阶段也是基于Promise A+规范来写的啦。
不多废话,接下来让我们进入手写阶段。
二、Promise核心逻辑实现
javascript">const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("success");
reject("err");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("resolve", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("reject", reason);
}
);
1.基本原理
Promise 是一个类,在执行这个类的时候会传入一个执行器,这个执行器会立即执行
Promise 会有三种状态
Pending 等待
Fulfilled 完成
Rejected 失败
状态只能由 Pending --> Fulfilled 或者 Pending --> Rejected,且一但发生改变便不可二次修改;
Promise 中使用 resolve 和 reject 两个函数来更改状态;
then 方法内部做但事情就是状态判断
如果状态是成功,调用成功回调函数
如果状态是失败,调用失败回调函数
2.新建类promise类,传入执行器executor
class myPromise {
constructor(executor) {
// 初始状态
this.state = "pending";
// 成功的值
this.value = null;
// 失败的值
this.reason = null;
try {
executor(this.resolve, this.reject);
} catch (error) {
this.reject(error);
}
}
3.传入resolve和reject方法
javascript">// 成功
resolve = (value) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = value;
}
};
// 失败
reject = (reason) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "rejected";
this.reason = reason;
}
};
4.then方法的简单实现
javascript">then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
}
5.完整代码及验证
完整代码:
javascript">class myPromise {
constructor(executor) {
// 初始状态
this.state = "pending";
// 成功的值
this.value = null;
// 失败的值
this.reason = null;
try {
executor(this.resolve, this.reject);
} catch (error) {
this.reject(error);
}
}
// 成功
resolve = (value) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = value;
}
};
// 失败
reject = (reason) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "rejected";
this.reason = reason;
}
};
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
}
}
验证:
javascript">new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("success");
// reject("err");
}).then(
(res) => {
console.log(res);
},
(err) => {
console.log(err);
}
);

可以看到这时,一个最简单的promise就实现啦。但大家有没有发现一个问题呢?上面的代码在调用then方法以后,只有fulfilled和rejected状态才会发生回调。
大家都知道,then方法是微任务,是要比宏任务先执行的,而promise状态改变是发生在resolve或reject之后的,那么如果我在setTimeout里去调用resolve,then方法就会在resolve之前执行,此时的状态为pending,那么我们的then方法不就没用了吗?
6.代码改进
上面说到,若处理同步任务时,then比resolve先执行,那么将会失败。
所以我们需要在then方法里面加上pending状态的回调,回调中将成功的回调和失败的回调对应添加到数组里,然后在状态改变时执行数组的每一项,代码如下:
javascript">class myPromise {
constructor(executor) {
// 初始状态
this.state = "pending";
// 成功的值
this.value = null;
// 失败的值
this.reason = null;
// 成功回调数组
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
// 失败回调数组
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
try {
executor(this.resolve, this.reject);
} catch (error) {
this.reject(error);
}
}
// 成功
resolve = (value) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
// 失败
reject = (reason) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "rejected";
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 声明返回的promise2
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
onRejected(this.reason);
});
}
}
}
让我们来验证一下:
javascript">new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("success");
}, 0);
// reject("err");
}).then(
(res) => {
console.log(res);
},
(err) => {
console.log(err);
}
);

成功!
三.链式调用
链式调用,也是promise里最重要的一点,解决回调地狱!
1.链式调用实现的基本思路
首先我们来验证一下之前写的代码能不能进行链式调用
javascript">const promise = new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("success");
}, 0);
});
promise
.then((value) => {
console.log(1);
console.log("resolve", value);
})
.then((value) => {
console.log(2);
console.log("resolve", value);
})
.then((value) => {
console.log(3);
console.log("resolve", value);
});
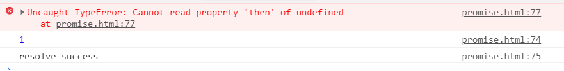
很明显,它不能。
我们要实现的话,应该先研究一下它的思路:
then 方法要链式调用那么就需要返回一个 Promise 对象
then 方法里面 return 一个返回值作为下一个 then 方法的参数,如果是 return 一个 Promise 对象,那么就需要判断它的状态
2.then方法返回promise对象
javascript">then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 声明返回的promise2
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
// 返回promise,完成链式
return promise2;
}
由代码可以看到,我们已经可以写出链式调用的伪代码了,现在我们需要编写resolvePromise方法,这里的resolvePromise函数是用来判断x的函数,若x是promise,取它的结果为新的promise2结果,否则直接作为promise2的结果。
3.resolvePromise方法
javascript">resolvePromise = (promise2, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 若x=promise2,则会一直循环套用
if (x === promise2) {
return reject(new TypeError("不能相等"));
}
// 防止多次调用
let called;
// x不是null 且x是对象或者函数
if (x != null && (typeof x === "object" || typeof x === "function")) {
try {
// 如果then是函数,就默认是promise了
if (typeof x.then === "function") {
x.then(
(y) => {
// 成功和失败只能调用一个
if (called) return;
called = true;
// resolve的结果依旧是promise 那就继续解析
this.resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
},
(err) => {
// 成功和失败只能调用一个
if (called) return;
called = true;
reject(err); // 失败了就失败了
}
);
}
} catch (e) {
if (called) return;
called = true;
// 取then出错了那就不要在继续执行
reject(e);
}
} else {
resolve(x);
}
};
这下就大功告成啦,让我们来试一试它能不能进行链式调用
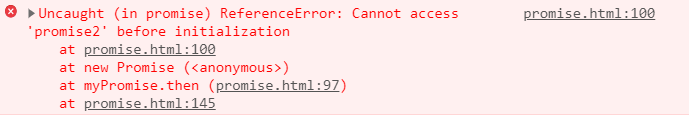
果然成功的路不是一帆风顺了,让我们来看看它到底是个啥问题。
从报错信息得知,我们在promise2初始化之前就去调用它了。我们看一看then方法里的代码
javascript">then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 声明返回的promise2
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
// 返回promise,完成链式
return promise2;
}
}
很明显!这个时候我们就要用上宏微任务和事件循环的知识了,这里就需要创建一个异步函数去等待 promise2 完成初始化。这里我们使用queueMicrotask来创建微任务。
javascript">then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 声明返回的promise2
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
queueMicrotask(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
queueMicrotask(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
}
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
});
});
}
});
// 返回promise,完成链式
return promise2;
}
我们给myPromise加上resolve和reject方法!
javascript">// resolve方法
myPromise.resolve = function (val) {
return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(val);
});
};
//reject方法
myPromise.reject = function (val) {
return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(val);
});
};
现在我们再来试一试能不能成功!
javascript"> myPromise
.resolve()
.then(() => {
console.log(0);
return myPromise.resolve(4);
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
});
myPromise
.resolve()
.then(() => {
console.log(1);
})
.then(() => {
console.log(2);
})
.then(() => {
console.log(3);
})
.then(() => {
console.log(5);
})
.then(() => {
console.log(6);
});
这里我用了一道非常经典的任务队列和promise题,来试一试我们的输出。
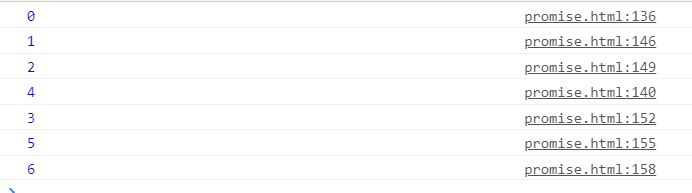
可以发现我们的链式调用成功啦!
四.总结
其实最后一道样例测试题是有疑问的,我使用了promises-aplus-tests测试我的promise是否符合A+规范,是通过的,但打印出来的顺序却和原生promise不一样,原生的是0123456,我的却是0124356。希望这个问题有大佬可以解答。
虽然这个问题还没有解决,但通过这次钻研,让我对promise的底层有了更深层次的了解,过程往往比结果更加重要,也希望大家能够讨论一下这道题,谢谢。





