JS 基础: typeof & instanceof 类型检查
文章目录
简介
写过几篇有关 JS 语言特性的博客,也研究过一些 ES6 相关的新特性。但是现在回头来看看我真的够了解 JS 里面的类型检查吗?由于 JS 属于弱类型动态语言,平常都用 var、let、const 声明变量就完事了,但是若我们想加强代码的健壮性和可用性,势必要在方法前对于不同的参数进行类型检查,并根据不同类型有相应的处理。好讲白了就是使用 typeof、instanceof 两个关键字就对了,马上来看看它们到底在干嘛。
参考
| JS中typeof与instanceof的区别 | https://www.cnblogs.com/Trr-984688199/p/6180040.html |
| js中typeof与instanceof用法 | https://www.cnblogs.com/double405/p/5326311.html |
正文
typeof 关键字
先来看看 typeof 这个关键字,比较简单。
稍微用过或是看过 JS(没看过猪跑至少吃过猪肉(bushi),都知道在 JS 中有九个基本类型(算上 undefined 和 Symbol):number、boolean、string、array、object、function、null、undefined、Symbol(ES6 新增);同时也存在一些内置函数作为构造函数:Number、Boolean、String、Array、Object、Symbol 等。
typeof 关键字是一个一元操作符(加不加括号没差,语法解析正确就行),会返回参数变量的"类型"的字符串,然而这个类型可能有一点 bug,跟你想象中的不太一样。其实也没啥秘密,直接来看输出:
字面量类型判断
第一波先给出直接判断字面量的结果:
js">console.log('----- literal value -----')
console.log(`typeof 1: ${typeof 1}`) // 数字字面量
console.log(`typeof '1': ${typeof '1'}`) // 字符串字面量
console.log(`typeof true: ${typeof true}`) // 布尔值字面量
console.log(`typeof []: ${typeof []}`) // 数组字面量
console.log(`typeof {}: ${typeof {}}`) // 对象字面量
console.log(`typeof function () {}: ${typeof function () {}}`) // 方法字面量
console.log(`typeof () => {}: ${typeof (() => {})}`) // 箭头函数字面量
console.log(`typeof null: ${typeof null}`) // null
console.log(`typeof undefined: ${typeof undefined}`) // defined
- 输出结果
----- literal value -----
typeof 1: number
typeof '1': string
typeof true: boolean
typeof []: object
typeof {}: object
typeof function () {}: function
typeof () => {}: function
typeof null: object
typeof undefined: undefined
从输出我们可以看到几个特点(以下说明皆为个人理解和记忆方式,不一定正确hhh):
undefined自成一类null空指针,所以被归类为对象 object[]数组:这个就比较特别了,可能是因为历史缘故,又或是 JS 引擎内部保存并解析数组的方式造成的,由于除了基本类型之外 JS 所有东西都能被视为对象 object,数组便能够被视为拥有键 0 , 1 , 2 , . . . 0, 1, 2, ... 0,1,2,... 的一个特殊对象(还有一种对象叫做类数组对象(Array-like Object),这又是另一个故事了…),总而言之结论就是typeof [] = "object",记住就对了hhh
内置函数类型判断
前面提过,JS 也为这些基本类型提供内置函数(built-in function),然而这个内置函数同时能够作为构造函数,也能够作为一般函数使用,这时候构建出来的值的类型就大不相同了:
js">console.log('----- use constructor -----')
console.log(`typeof Number(1): ${typeof Number(1)}`)
console.log(`typeof new Number(1): ${typeof new Number(1)}`)
console.log(`typeof String('1'): ${typeof String('1')}`)
console.log(`typeof new String('1'): ${typeof new String('1')}`)
console.log(`typeof Boolean(true): ${typeof Boolean(true)}`)
console.log(`typeof new Boolean(true): ${typeof new Boolean(true)}`)
console.log(`typeof Array(10): ${typeof Array(10)}`)
console.log(`typeof new Array(10): ${typeof new Array(10)}`)
console.log(`typeof Object({}): ${typeof Object({})}`)
console.log(`typeof new Object({}): ${typeof new Object({})}`)
- 输出
----- use constructor -----
typeof Number(1): number
typeof new Number(1): object
typeof String('1'): string
typeof new String('1'): object
typeof Boolean(true): boolean
typeof new Boolean(true): object
typeof Array(10): object
typeof new Array(10): object
typeof Object({}): object
typeof new Object({}): object
我们可以看到如果将内置函数作为一般函数使用(例如 Number(xxx)),这时候构建出来的值相当于一个字面量,然而作为构造函数构造出来的仅仅是不同类型的另一个对象而已(这里指的是对象的类型,变量本身的类型必为对象 object)
typeof 小结
这边给出关于 typeof 关键字的小结:
typeof用于判断变量的类型,而不是对象的类型undefined自成一类:undefined类型null、array会被判断成对象 object
应用
由于 typeof 不能很好的识别数组和对象的差别,也看不出对象所属的类型(原型,下面会提到),所以 typeof 通常用于下面几种场景:
- 判断未定义 undefined:当然其实用
=== undefined也行,所以用处不大 - 判断对象 object:如果是对象才有能够访问的属性,也就是决定有没有属性能访问(属性访问符
.) - 判断函数 function:用于确定回调函数是否正确传入
instanceof 关键字
看完发现,typeof 好像有点废啊,尤其到了大家都在用 OOP 的时代,还不能判断对象的类型那可不行,因此我们就要请出第二个关键字 instanceof(是的没错 Java 里面也有一个,但是作用和含义大不相同:Java 使用的是基于类型的继承结构,而 JS 则是基于原型链,两者差了大概八千里远)
Prototype Chain 原型链回顾
在正式使用 instanceof 关键字之前,我们先来回顾以下关于 JS 原型链的知识(也可以参考我之前写的 JS 基礎:Prototype Chain 原型鏈)
JS 的对象类型是基于原型链,这边就不再展开解说,我们的重点摆在内置函数之间的继承(原型)关系
内置函数的原型链
前面我们提到各个类型的内置函数,同时就是构造函数,同时就是类型(划重点,这个真的很重要)!
原型链的类型信息就是指当前对象的原型对象(proto),我们可以通过非正式但是通用的属性 __proto__ 来访问得到:
js">const nc = Number
const sc = String
const bc = Boolean
const ac = Array
const oc = Object
console.log(nc)
console.log(nc.prototype)
console.log(nc.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(sc)
console.log(sc.prototype)
console.log(sc.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(bc)
console.log(bc.prototype)
console.log(bc.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(ac)
console.log(ac.prototype)
console.log(ac.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(oc)
console.log(oc.prototype)
console.log(oc.prototype.__proto__)
console.log('----- compare -----')
console.log(nc.prototype.__proto__ === sc.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(nc.prototype.__proto__ === bc.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(nc.prototype.__proto__ === ac.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(nc.prototype.__proto__ === oc.prototype)
这边我们使用浏览器的输出能够看得更清楚:
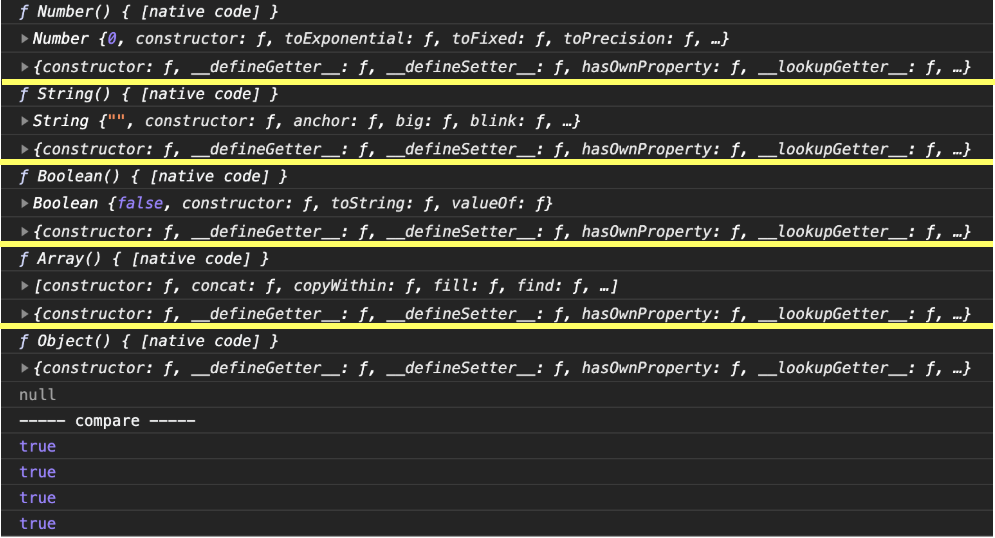
我们可以看到各个内置函数的原型链,输出太乱了,画张图吧(上一篇 里有完整的大图,这边重画一次)

prototype__proto___175">属性规则:prototype、__proto__
我们可以看到通常是构造函数的 prototype 指向原型对象,对象实例(可能同时作为某个对象的原型)则透过 __proto__ 指向它的原型对象,所有对象的原型链顶部必定存在 Object.prototype 指向的对象,而这个对象的 __proto__ 属性则为 null
instanceof 实例
讲了半天的原型链,现在回到我们的主题 instanceof 关键字。
instanceof的关键字检查的便是当前对象的原型链上是否存在指定类型(原型对象)
好看起来有点难懂,首先我们透过上一篇明确所谓的对象类型,便是原型链上的一个个对象,instanceof 则会为我们检查这个链上有没有目标类型(一个原型对象),使用语法如下:
js"><object> instanceof <constructor>
注意这边的第二个参数不是直接传入那个对象,而是某个构造函数,所以 instanceof 关键字实际上做的事应该这样说:
说了半天越说越糊涂了,赶紧来看代码hhh
js">const n = new Number(1)
console.log(n)
console.log(n.__proto__)
console.log(n.__proto__.__proto__)
console.log(n.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__)
console.log(`1 instanceof Number: ${1 instanceof Number}`)
console.log(`n instanceof Number: ${n instanceof Number}`)
- 输出
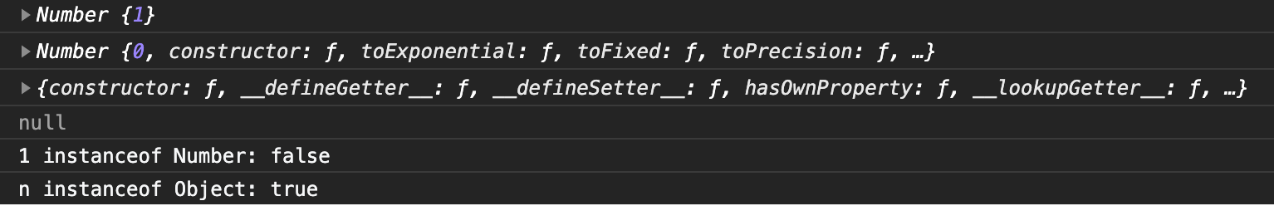
和我们预想的一样:字面量 1 不是对象,所以啥也不是,必须为 false;而 n 使用 Number 构造出来的对象,所以它的原型链应该为:
n -> Number.prototype -> Object.prototype -> null
最后一句 n instanceof Number 会查找 Number.prototype 是否在 n 的原型链上,第一个就是所以返回 true
添加新类型
看过使用内置函数创建的数字(Number)对象,接下来我们自己写一个整数类型(Integer) 来加深我们对于 instanceof 的应用
prototype_225">直接指向 Number.prototype
首先我们第一个想到的就是,直接写一个构造函数,然后把它的原型变成 Number.prototype 不就成了吗,马上来试试:
js">function Integer (num) {
this.value = Math.floor(num)
}
Integer.prototype = Number.prototype
const n = new Number(1)
const i = new Integer(123)
console.log(i)
console.log('----- Integer.prototype = Number.prototype -----')
console.log(`i instanceof Number: ${i instanceof Number}`)
console.log(`i instanceof Integer: ${i instanceof Integer}`)
console.log(`n instanceof Number: ${n instanceof Number}`)
console.log(`n instanceof Integer: ${n instanceof Integer}`)
- 输出
----- Integer.prototype = Number.prototype -----
i instanceof Number: true
i instanceof Integer: true
n instanceof Number: true
n instanceof Integer: true
咦?好像有个小 bug,n 怎么也变成 Integer 类型了?
这是因为我们直接写了 Integer.prototype = Number.prototype,也就是说我们只是创建了 Number 类型的另一个构造函数 Integer,也就是说原型链张成下面这样:
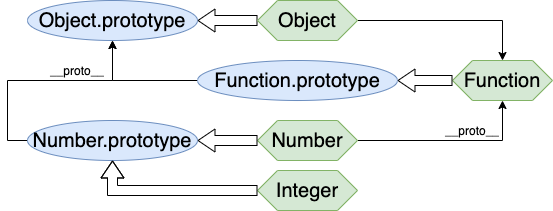
下面我们来看看真正的继承
继承 Number
上面的实现其实不太对,Integer 应该作为 Number 的子类(使用 is a 来判断:一个 Integer 是 Number,而一个 Number 不一定是 Integer)
也就是说我们应该创建一个新类型(再次强调,类型就是原型对象),我们应该要将原型链做成下面这样:
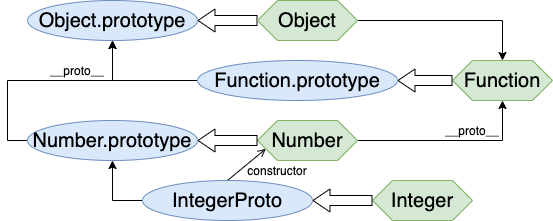
js">function Integer (num) {
this.value = Math.floor(num)
}
const IntegerProto = new Number()
Integer.prototype = IntegerProto
const n = new Number(1)
const j = new Integer(456)
console.log('----- Integer.prototype = IntegerProto -----')
console.log(`j instanceof Number: ${j instanceof Number}`)
console.log(`j instanceof Integer: ${j instanceof Integer}`)
console.log(`n instanceof Number: ${n instanceof Number}`)
console.log(`n instanceof Integer: ${n instanceof Integer}`)
- 输出
----- Integer.prototype = IntegerProto -----
j instanceof Number: true
j instanceof Integer: true
n instanceof Number: true
n instanceof Integer: false
好的大功告成啦!我们成功继承了 Number,并区别出 Number 和 Integer 的类层次关系了(j 是 Integer 也是 Number;n 是 Number 但不是 Integer)
完善 Integer
最后的最后我们完善以下我们的 Integer 类型,并在其中加入类型判断,使其能够接受 (1) 一般的数字也能够接受 (2) Integer 类型的对象作为参数
一般版本
js">function Integer (num) {
this.value = Math.floor(num)
}
Integer.prototype = new Number() // 继承 Number
Integer.prototype.add = function (num) {
// 传入参数为 number
if (typeof num === 'number') {
num = Math.floor(num)
this.value = this.value + num
// 传入为 Integer 实例
} else if (num instanceof Integer) {
this.value = this.value + num.value
// 不接受其他类型
} else {
throw new TypeError('expect number or Integer for function add')
}
console.log(`add ${num} => ${this.value}`)
return this
}
Integer.prototype.sub = function (num) {
if (typeof num === 'number') {
num = Math.floor(num)
this.value = this.value - num
} else if (num instanceof Integer) {
this.value = this.value - num.value
} else {
throw new TypeError('expect number or Integer for function sub')
}
console.log(`sub ${num} => ${this.value}`)
return this
}
Integer.prototype.mul = function (num) {
if (typeof num === 'number') {
num = Math.floor(num)
this.value = this.value * num
} else if (num instanceof Integer) {
this.value = this.value * num.value
} else {
throw new TypeError('expect number or Integer for function mul')
}
console.log(`mul ${num} => ${this.value}`)
return this
}
Integer.prototype.div = function (num) {
if (typeof num === 'number') {
num = Math.floor(num)
this.value = Math.floor(this.value / num)
} else if (num instanceof Integer) {
this.value = Math.floor(this.value / num.value)
} else {
throw new TypeError('expect number or Integer for function div')
}
console.log(`div ${num} => ${this.value}`)
return this
}
Integer.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.value
}
const i = new Integer(1)
console.log(`i = ${i}`)
console.log(`i instanceof Integer: ${i instanceof Integer}`)
console.log(`i instanceof Number: ${i instanceof Number}`)
i.add(15).sub(new Integer(4)).mul(5).div(new Integer(13.579))
- 输出
i = 1
i instanceof Integer: true
i instanceof Number: true
add 15 => 16
sub 4 => 12
mul 5 => 60
div 13 => 4
Currying 科里化定义
我们发现上面的定义重复性相当高,因此我们就可以抽象出一个方法生成函数(借鉴 Currying 科里化的思想)
js">function Integer (num) {
this.value = Math.floor(num)
}
Integer.prototype = new Number() // 继承 Number
// 两个参数的操作抽象
Integer.prototype.binary_operation = function (name, calc) {
return (num) => {
if (typeof num === 'number') {
num = Math.floor(num)
this.value = Math.floor(calc(this.value, num))
} else if (num instanceof Integer) {
this.value = Math.floor(calc(this.value, num.value))
} else {
throw new TypeError('expect number or Integer for function add')
}
console.log(`${name} ${num} => ${this.value}`)
return this
}
}
// 科里化调用
Integer.prototype.add = function (num) { return this.binary_operation('add', (x, y) => x + y)(num) }
Integer.prototype.sub = function (num) { return this.binary_operation('sub', (x, y) => x - y)(num) }
Integer.prototype.mul = function (num) { return this.binary_operation('mul', (x, y) => x * y)(num) }
Integer.prototype.div = function (num) { return this.binary_operation('div', (x, y) => x / y)(num) }
Integer.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.value
}
const i = new Integer(1)
console.log(`i = ${i}`)
console.log(`i instanceof Integer: ${i instanceof Integer}`)
console.log(`i instanceof Number: ${i instanceof Number}`)
i.add(15).sub(new Integer(4)).mul(5).div(new Integer(13.579))
- 输出
i = 1
i instanceof Integer: true
i instanceof Number: true
add 15 => 16
sub 4 => 12
mul 5 => 60
div 13 => 4
结语
本篇本来就是想简单介绍以下 typeof 跟 instanceof 的用法,贴几个输出就完事了hh,没想到突然脑洞大开加了一个 Integer 进去,也是加深对两个关键字的理解吧(确定馁hh)。